5G Networks
Evolve to the Next Generation of Wireless
Deploying a 5G Network
As the number of connected devices grows and the connectivity needs of Communications Service Providers (CSPs) and business networks shift towards higher throughput, security, and reliability, the evolution from Evolved Packet Core (EPC) to 5G Core (5GC) and RAN will be central in meeting the needs of new services and applications. 5G Non-Stand-Alone (5G NSA) and Stand-Alone (5G SA) will open a new universe of possibilities for differentiation and business.
Overview
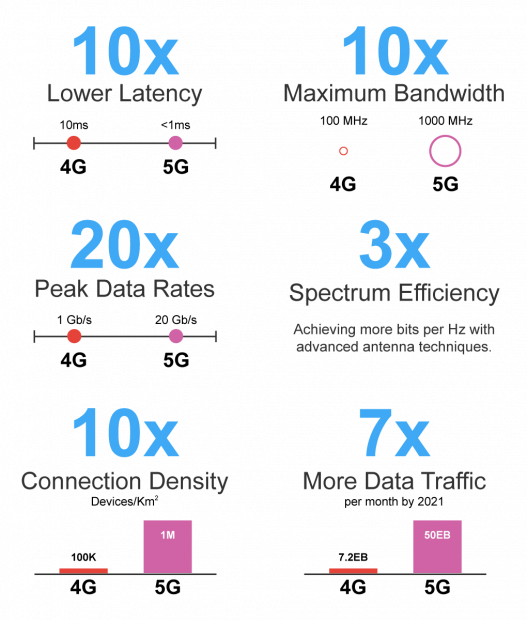
5G – the next evolution of cellular technology is revolutionizing the way that businesses and mobile users interact with the world around them. With significantly more capacity for moving data, ultra-low latency, and the added ability to connect to a multitude of different devices at once, 5G may fundamentally change the way we live, work and communicate.
The evolution to 5G will rely on multiple steps, including:
- virtualization of core network functions for Packet Core, IMS and subscription management
- separation of control and user plane functions
- introduction of network slicing, enabling multiple logical networks to be supported over one network platform
- distribution of cloud infrastructure closer to users
- consolidation of user plane functions for mobile, fixed wireless and fixed access
These architecture changes will be critical to achieving the targeted 5G network that meets the business’s and CSPs’ needs.
Building Blocks of 5G
Operations and Management
- Efficiently operate a cloud based platform with new ways of working and evolved processes
- Transform operations to reach the 5G network’s full potential
5G Core
- Establish a core platform built on cloud-based technology that combines EPC and 5G core network functions
- Reach deployment flexibility and TCO efficiency during the 5G migration
Cloud Based Infrastructure
- Deploy a system-verified cloud infrastructure solution optimized for cloud applications
- Reduce risks while building this cloud platform for 5G services
Network Security
- Safeguard networks with a secure design and monitoring to protect against external threats
- Create a safe innovation ecosystem to capture new business opportunities
5G Voice
- Leverage 4G voice solutions via VoLTE and enable high-quality 5G voice
- Expand with new 5G communication service capabilities
Evolved Network Elements
5G System Architecture
5G’s Network Architecture leverages web and cloud technologies to offer modularity, scalability, reliability, cost-effective operation, easy deployments, and faster innovation between all of the interconnected Network Functions (NF). This evolution in 5G architecture represents a shift from telecom-type interfaces to web-based APIs for the control functions, offering a complete service mesh with service discovery, load balancing, encryption, authentication and authorization.
AUSF
Authentication Server Function
The AUSF performs authentication function similar to 4G HSS with a UE. It implements the EAP authentication server and stores keys.
UDM
Unified Data Management
Analogous to the HSS, the UDM is cloud-native and designed for 5G specifically. Manages data for access authorization, user registration, and data network profiles, providing authentication credentials while being employed by the AMF and SMF to retrieve subscriber data and context. Can be paired with the User Data Repository (UDR) which stores the user data such as customer profile information.
AMF
Access and Mobility Management Function
The AMF serves part of the role of the 4G MME, that of mobility management. The AMF maintains a NAS signaling connection with the UE and manages the UE registration procedure. The AMF is also responsible for paging.
SMF
Session Management Function
The SMF is primarily responsible for interacting with the decoupled data plane, creating updating and removing Protocol Data Unit (PDU) sessions and managing session context with the User Plane Function (UPF).
PCF
Policy Control Function
The PCF helps Operators and CSPs easily create and deploy policies to govern network behavior in in a 5G Network. The PCF accesses the subscription information, required to make policy decisions, from the UDM and then provides the appropriate policy rules to the control plane functions so that they can enforce them.
UPF
User Plane Function
Analogous to the SGW-U and PGW-U of 4G Network, the UPF performs user plane operations such as maintaining PDU Session, Packet routing & forwarding, Packet inspection, Policy enforcement for User plane, QoS handling, etc, based on information received from the SMF. The UPF allows packet processing and traffic aggregation to be performed closer to the network edge, increasing bandwidth efficiencies while reducing network strain.
AF
Application Function
style = "padding-top:12px;"Analogous to the AF in an EPC, the 5G AF performs operations like accessing Network Exposure Function for retrieving resources, interaction with PCF for Policy Control, Applications Traffic Routing, Exposing services to End users, etc.
DN
Data Network
The DN identifies Service Provider services, Internet access or 3rd party services.
Select a core technology to learn more
Paths to 5G
There are several paths to reach a 5G network. Each will include different objectives in terms of new technology introduction, use cases and time frames. The two main paths, 5G Non-standalone (NSA) and 5G standalone (SA) are two 5G tracks that communication service providers can opt for when transitioning from 4G to the next-generation mobile technology. 5G NSA is an enhanced EPC that leverages 5G ready Radio solutions capable of communicating with 5G ready devices. 5G SA is true 5GC (5G Core) that brings all possible use cases to the 5G mobile network, such as high throughput, low latency communications, massive IoT, network slicing, and more.
The target mobile network and desired applications will be what shapes the strategy that CSPs and operators will decide upon when deploying their 5G network.
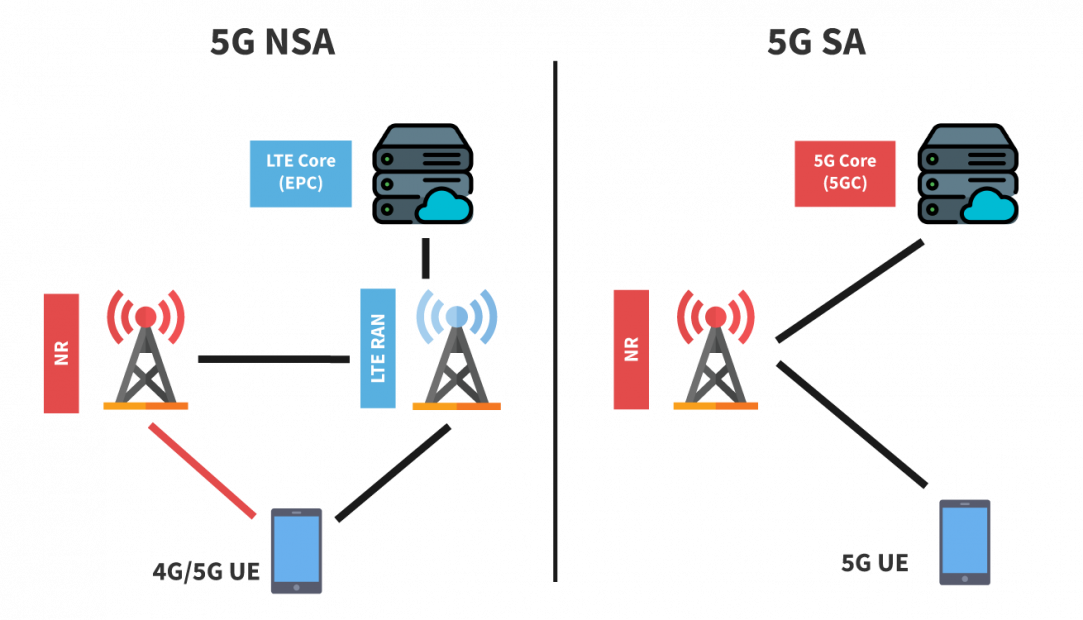
Benefits of 5G NSA:
- Maximizes the use of the existing installed LTE base
- Provides early adopter with 5G-enabled devices
- Easiest way to enter 5G space and gain technology and market leadership
- Higher broadband speeds will enable more capacity and delivery efficiency
Benefits of 5G SA:
- Simplified RAN and device architecture
- Introduces ultra-low latency and high reliability communications
- Supports advanced network-slicing functions for enhanced mobile broadband, massive machine-to-machine communications, and massive IoT
- Multi-gigabit data rates with improved efficiency and lower costs
Features & Interfaces
AMF (Access and Mobility Management function)
- Registration Management
- Connection Management
- Mobility Management
- Authentication
- NAS ciphering and integrity protection
SMF (Session Management Function)
- PDU Session establishment/modification/release
- Multiple QoS flows per PDU session
- Multiple sessions for each SUPI
- UE IP address allocation using DHCP, local IP pools, static IP.
- Bandwidth control
- Multiple DNN support
UDM/AUSF (Unified Data Management/Authentication Server Function)
- Generation of 3GPP AKA Authentication Credentials
- User Identification Handling (e.g. storage and management of SUPI for each
subscriber in the 5G system) - UE’s Serving NF Registration Management (e.g. storing serving AMF for UE, storing
serving SMF for UE’s PDU Session) - Subscription management
- Supports authentication for 3GPP access
UPF (User Plane Function)
- Packet routing and forwarding
- Packet inspection, QoS handling
- External PDU session for interconnecting Data Network (DN)
- PDU session anchor point for transport within and between Radio access Technologies.
- Traffic usage reporting for billing and Lawful Intercept (LI)




